Delve into the fascinating world of foreign exchange trading with our comprehensive guide, “Foreign Exchange Market Real Examples.” This detailed resource empowers you with the knowledge and insights necessary to navigate the complexities of the global currency market, equipping you for informed decision-making and successful trading.
Throughout this guide, we will explore the intricacies of the foreign exchange market, from its history and participants to the factors that influence currency exchange rates. We will delve into the various trading methods and strategies employed by experienced traders, empowering you with the tools to make informed choices in your own trading endeavors.
Overview of the Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market, also known as Forex or FX, is a global marketplace where currencies are traded. It is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume of over $5 trillion.
Investigate the pros of accepting bis foreign exchange market turnover in your business strategies.
The purpose of the foreign exchange market is to facilitate the exchange of currencies for various reasons, including international trade, investment, and tourism. It allows businesses and individuals to convert one currency into another at a predetermined exchange rate.
Obtain access to list three functions of foreign exchange market to private resources that are additional.
Types of Participants
The foreign exchange market consists of a diverse range of participants, including:
- Banks: Commercial and investment banks are the primary participants in the foreign exchange market, facilitating currency transactions for their clients.
- Institutional Investors: Hedge funds, mutual funds, and pension funds participate in the foreign exchange market to manage their currency risk and enhance returns.
- Corporations: Multinational corporations use the foreign exchange market to exchange currencies for cross-border transactions and manage their foreign exchange exposure.
- Retail Traders: Individual traders participate in the foreign exchange market through online platforms, speculating on currency price movements.
- Central Banks: Central banks intervene in the foreign exchange market to influence exchange rates and manage their country’s monetary policy.
Brief History
The foreign exchange market has evolved over centuries, with its origins in the exchange of coins and precious metals. In the 20th century, the gold standard system pegged currencies to the value of gold, but this system collapsed in the 1970s.
Since then, the foreign exchange market has operated under a floating exchange rate system, where currency values are determined by supply and demand. The development of electronic trading platforms in the 1990s and 2000s has significantly increased the volume and efficiency of foreign exchange transactions.
Obtain direct knowledge about the efficiency of foreign exchange market ap macro through case studies.
Factors Affecting Foreign Exchange Rates
The foreign exchange market is a complex and dynamic system, and the factors that affect foreign exchange rates are just as diverse. These factors can be broadly classified into three main categories: economic, political, and psychological.
Economic Factors
Economic factors are the most fundamental drivers of foreign exchange rates. These factors include:
- Interest rates: Interest rates are the cost of borrowing money. Higher interest rates make a country’s currency more attractive to investors, as they can earn a higher return on their investments. This increased demand for the currency will lead to an appreciation in its value.
- Inflation: Inflation is the rate at which prices are rising. Higher inflation can lead to a depreciation in a country’s currency, as investors become less confident in the stability of the economy.
- Economic growth: Economic growth is a measure of the overall health of an economy. Strong economic growth can lead to an appreciation in a country’s currency, as investors become more confident in the future prospects of the economy.
- Trade balance: A trade balance is the difference between a country’s exports and imports. A positive trade balance means that a country is exporting more goods and services than it is importing, which can lead to an appreciation in its currency.
Methods of Trading Foreign Exchange
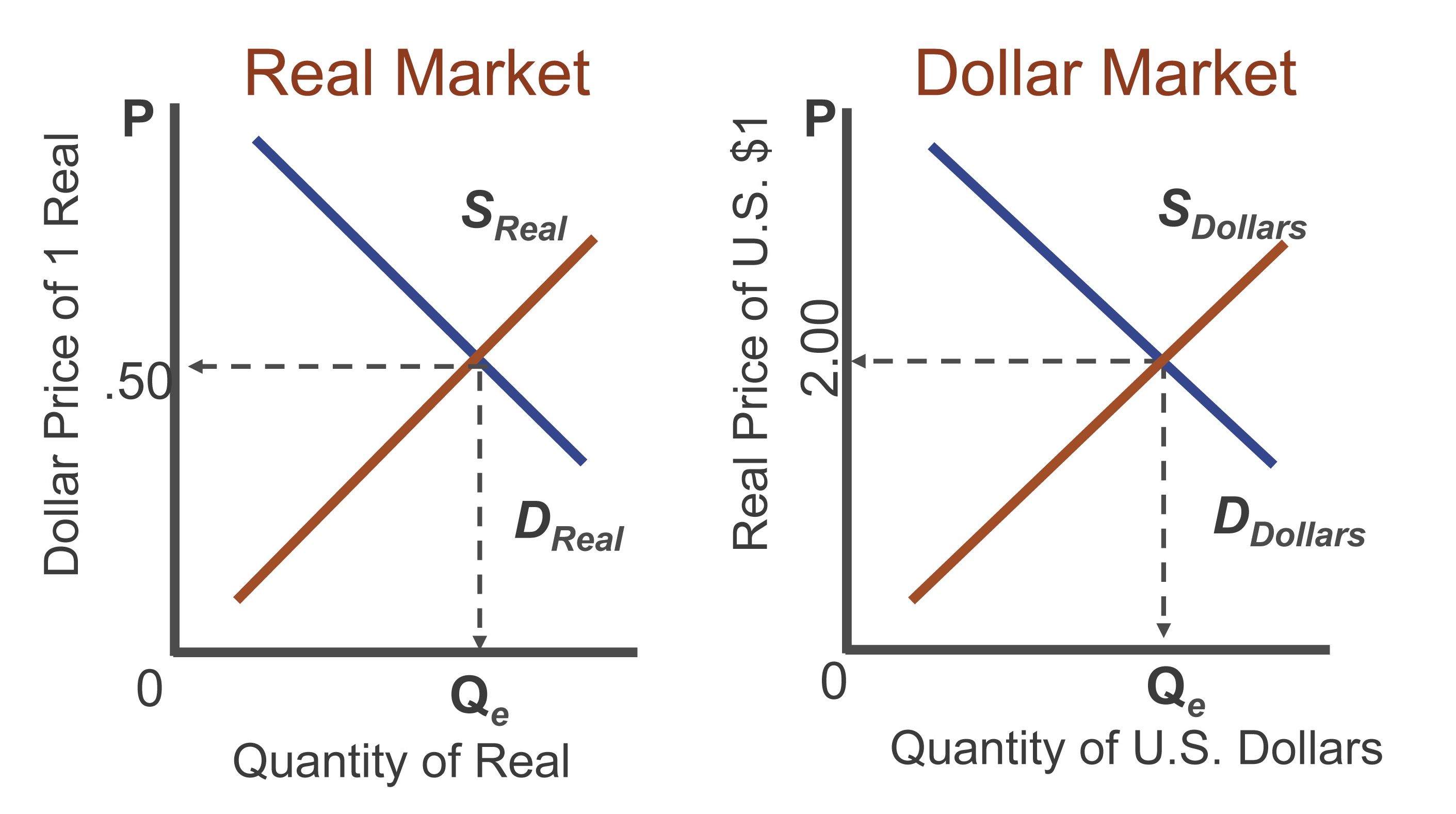
Foreign exchange trading involves buying and selling currencies to make a profit from fluctuations in their exchange rates. There are different types of trading orders, platforms, and strategies used in foreign exchange trading.
Types of Foreign Exchange Trading Orders
- Market Order: Executes the trade immediately at the current market price.
- Limit Order: Specifies the price at which the trader is willing to buy or sell the currency.
- Stop Order: Triggers a market order when the price reaches a specified level.
Types of Foreign Exchange Trading Platforms
- Over-the-Counter (OTC): Trades are conducted directly between two parties, typically through a broker.
- Electronic Communication Network (ECN): Centralized marketplaces that match buyers and sellers electronically.
- Forex Broker: Intermediaries that provide access to the foreign exchange market and offer various services.
Strategies Used in Foreign Exchange Trading
- Scalping: Taking small profits from short-term price fluctuations.
- Trend Following: Trading in the direction of the prevailing market trend.
- Range Trading: Buying and selling within a defined price range.
- Carry Trade: Borrowing in a low-interest currency and investing in a high-interest currency to profit from the interest rate differential.
Risks and Rewards of Foreign Exchange Trading
Foreign exchange (forex) trading offers potential rewards but also carries risks. Understanding both is crucial for successful trading.
Risks Associated with Foreign Exchange Trading
- Market Volatility: Forex markets are highly volatile, and prices can fluctuate rapidly due to various factors.
- Leverage: Forex trading often involves leverage, which amplifies both potential gains and losses.
- Counterparty Risk: Forex transactions rely on counterparties to fulfill their obligations, and default risk exists.
- Transaction Costs: Trading fees, spreads, and other costs can impact profitability.
- Economic and Political Factors: Global economic events and political developments can significantly influence currency values.
Rewards of Foreign Exchange Trading, Foreign exchange market real examples
- High Liquidity: Forex markets are highly liquid, allowing for quick and easy execution of trades.
- 24/5 Trading: Forex trading is available 24 hours a day, 5 days a week, providing flexibility.
- Profit Potential: Forex markets offer the potential for substantial profits due to leverage and market volatility.
- Diversification: Trading in different currencies can help diversify a portfolio and reduce overall risk.
- Educational Value: Forex trading can provide valuable insights into global markets and economic trends.
Tips for Managing Risk in Foreign Exchange Trading
- Use Stop-Loss Orders: Set orders to automatically close positions at a predetermined loss level to limit potential losses.
- Control Leverage: Use leverage cautiously and within your risk tolerance.
- Diversify Trades: Spread trades across different currency pairs and trading strategies to reduce exposure to any single risk factor.
- Monitor Market Conditions: Stay informed about economic and political events that may impact currency values.
- Manage Emotions: Avoid emotional trading decisions and stick to a disciplined trading plan.
Real-World Examples of Foreign Exchange Trading
The foreign exchange market is not just a theoretical concept; it has real-world implications for businesses, economies, and individuals. In this section, we will explore some case studies of successful foreign exchange traders, examine how foreign exchange trading has impacted businesses and economies, and compare different foreign exchange trading strategies.
Case Studies of Successful Foreign Exchange Traders
There are many successful foreign exchange traders who have made significant profits by leveraging their knowledge and skills in the market. Here are a few notable examples:
- George Soros: Soros is a Hungarian-American investor and philanthropist who is known for his success in foreign exchange trading. He is best known for his “breaking the Bank of England” trade in 1992, which earned him over $1 billion.
- Bill Lipschutz: Lipschutz is an American currency trader who is known for his success in the foreign exchange market. He is the founder of Hathersage Capital Management, a hedge fund that specializes in currency trading.
- Stanley Druckenmiller: Druckenmiller is an American investor and hedge fund manager who is known for his success in foreign exchange trading. He is the founder of Duquesne Capital Management, a hedge fund that has consistently outperformed the market.
Impact of Foreign Exchange Trading on Businesses and Economies
Foreign exchange trading can have a significant impact on businesses and economies. Here are a few examples:
- Businesses: Businesses that import or export goods and services are affected by foreign exchange rates. When the value of the currency in which they import goods increases, their costs increase. Conversely, when the value of the currency in which they export goods increases, their profits increase.
- Economies: Foreign exchange trading can also impact economies. For example, a country with a weak currency may experience inflation, as imported goods become more expensive. Conversely, a country with a strong currency may experience deflation, as exported goods become cheaper.
Comparison of Foreign Exchange Trading Strategies
There are a variety of foreign exchange trading strategies that traders can use. Here is a table comparing some of the most common strategies:
| Strategy | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trend following | This strategy involves identifying the trend of a currency pair and trading in the direction of the trend. | – Can be profitable in trending markets. – Relatively easy to implement. | – Can be unprofitable in ranging markets. – Can lead to large losses if the trend reverses. |
| Range trading | This strategy involves trading within a specific range of prices. | – Can be profitable in ranging markets. – Relatively low risk. | – Can be unprofitable in trending markets. – Can be difficult to identify the range. |
| Carry trading | This strategy involves borrowing money in one currency with a low interest rate and investing it in another currency with a higher interest rate. | – Can be profitable if the interest rate differential is large. – Relatively low risk. | – Can be unprofitable if the interest rate differential changes. – Can be risky if the currency pair moves against the trader. |
| Scalping | This strategy involves making small profits on a large number of trades. | – Can be profitable in volatile markets. – Relatively low risk. | – Can be difficult to implement. – Can be stressful. |
Concluding Remarks: Foreign Exchange Market Real Examples

As we conclude our exploration of the foreign exchange market, we hope you have gained a deeper understanding of its dynamics and the practical applications of foreign exchange trading. Whether you are a seasoned trader or just starting out, this guide has provided you with valuable insights and real-world examples to enhance your trading journey.
Remember, the foreign exchange market is a constantly evolving landscape, and staying informed is crucial for success. Continue to seek knowledge, monitor market trends, and refine your strategies to maximize your potential in this exciting and ever-changing arena.
